A 404 error occurs when a user or search engine attempts to access a webpage that no longer exists or was never available. While occasional 404 errors are normal, excessive broken links can negatively impact user experience (UX) and search engine optimization (SEO). As an expert in technical SEO, I will outline the best practices for identifying, fixing, and preventing 404 page not found gohighlevel errors to ensure a healthy website and strong rankings.
Understanding 404 Errors and Their SEO Impact
404 errors signal to both users and search engines that a requested resource is unavailable. While Google does not penalize websites for having some 404 errors, an excessive number of broken pages can cause the following issues:
- Reduced Crawl Efficiency: Search engines waste crawl budget on non-existent pages, potentially leading to important pages being ignored.
- Loss of Link Equity: Backlinks pointing to deleted pages may not pass authority if not properly redirected.
- Increased Bounce Rate: Users encountering frequent 404 errors may leave your site, increasing bounce rates and reducing engagement.
Understanding these risks underscores the importance of proactively managing and minimizing 404 errors.

Common Causes of 404 Errors
404 errors can arise due to various reasons, including:
- Deleted Pages Without Redirects: Removing content without a 301 redirect causes users to land on a dead page.
- URL Changes Without Proper Redirects: Changing URL structures (e.g., during site migration) without redirecting old URLs.
- Incorrect Internal Links: Mistyped URLs in navigation, anchor text, or menus leading to non-existent pages.
- External Links to Non-Existent Pages: Backlinks from other websites pointing to outdated or incorrect URLs.
- Server Misconfigurations: Issues in the
.htaccessfile, web.config, or server settings resulting in unintended 404 errors.

How to Identify 404 Errors on Your Website
Before fixing 404 errors, you need to detect them using reliable tools:
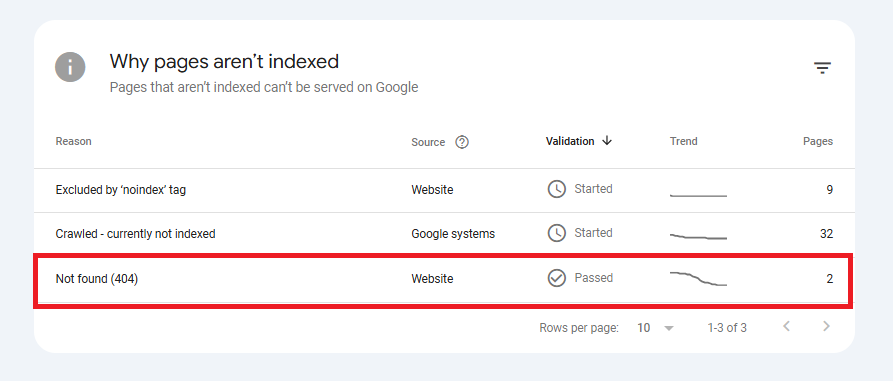
- Google Search Console (GSC): Check the “Coverage” section for reported 404 errors.
- Website Crawlers (Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, Semrush, Ahrefs): Identify broken internal links and missing pages.
- Google Analytics: Create a custom report to track users landing on 404 pages.
- Server Logs & Monitoring Tools (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana): Detect 404 error patterns.
Regular monitoring of these tools ensures early detection and quicker resolution of 404 issues.
Best Practices for Fixing 404 Errors
Once you identify broken pages, follow these strategies to fix them effectively:
1. Implement 301 Redirects for Moved or Deleted Pages
A 301 redirect is the best way to direct users and search engines from an old URL to a new one. Best practices include:
- Redirecting to the most relevant existing page (not just the homepage).
- Avoiding long redirect chains that slow down page loading.
- Using wildcard redirects for pattern-based URL changes.
2. Use 410 Status for Permanently Removed Pages
If a page no longer serves any purpose, a 410 (Gone) status tells search engines that the page was intentionally removed and should be deindexed faster than a 404.
3. Fix Internal Broken Links
- Run regular audits to identify and correct broken internal links.
- Update outdated links within blog posts, menus, and XML sitemaps.
- Ensure your CMS (WordPress, Shopify, etc.) doesn’t generate incorrect URLs.
4. Manage External Links Effectively
- Outreach: Contact website owners linking to broken URLs and provide updated links.
- Redirect Strategy: If external sites don’t update links, use a redirect instead of leaving them broken.
- Monitor Backlinks: Tools like Ahrefs or Moz can help track and fix inbound broken links.
5. Optimize Your 404 Error Page
A custom 404 page improves user experience and reduces bounce rates. Key elements to include:
- A friendly, helpful message (e.g., “Oops! This page doesn’t exist, but here’s what you can do next.”)
- Navigation links to important pages like Home, Blog, and Contact.
- A search bar to help users find relevant content.
- Engaging design with branding and humor (if appropriate).
Preventing Future 404 Errors
Prevention is more efficient than repeatedly fixing 404 errors. Here are strategies to minimize future broken links:
1. Implement URL Change Management
- Maintain a spreadsheet of old and new URLs during site migrations.
- Use canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues.
- Plan content updates without unnecessary URL changes.
2. Automate Website Monitoring
- Set up automated alerts for broken links using tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs.
- Integrate server monitoring tools for real-time error detection.
3. Audit Your Website Regularly
- Perform a quarterly website audit using crawling tools to identify broken links.
- Update outdated content and internal links to keep URLs active and relevant.
4. Train Your Team on SEO Best Practices
- Educate content managers and developers on the importance of URL consistency.
- Ensure proper redirect implementation when updating content.
- Avoid unnecessary URL restructuring without proper planning.
Technical Implementation Tips
For those managing 404 errors at a technical level, ensure the following:
- Use .htaccess (Apache) or web.config (IIS) for redirects.
- Monitor redirect response times to prevent excessive redirects slowing down site performance.
- Ensure proper HTTP headers are set for accurate crawl signals.
Tracking and Documentation
Maintaining a log of 404 errors and resolutions is essential for long-term success:
- Document original broken URLs, implemented redirects, and date of fix.
- Use Google Sheets or SEO tracking software to organize and track fixes.
- Review historical data to identify trends in recurring 404 errors.
Final Thoughts
Effective 404 error management is critical for both user experience and SEO. While some broken links are unavoidable, proactively identifying, fixing, and preventing 404 errors will help maintain your site’s health and search rankings.
By following the strategies outlined in this guide—implementing 301 redirects, auditing links, monitoring errors, and optimizing 404 pages—you can ensure a seamless user experience while maximizing your site’s visibility in search engines.
Regular maintenance and continuous optimization are key to long-term SEO success. Keep monitoring, updating, and refining your approach, and your website will remain error-free and highly optimized!