Google Search Console VS Rapid URL Indexer
| Feature | Google Search Console | Rapid URL Indexer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Manage a website’s Google presence. | Speed up URL indexing. |
| Cost | Free. | Paid, with various pricing plans. |
| URL Indexing Speed | Slow (days to weeks). | Fast (minutes to hours). |
| Bulk URL Submission | Limited. | Supports bulk submissions. |
| Search Engine Coverage | Google only. | Google, Bing, Yahoo, etc. |
| Ease of Use | Requires some technical knowledge. | Beginner-friendly interface. |
| Additional Features | Analytics, performance monitoring. | Focused solely on indexing. |
If you’re looking to speed up URL indexing, especially for high volumes of content, Rapid URL Indexer is a valuable tool. It complements Google Search Console, ensuring faster indexing and broader coverage across multiple search engines, making it a beneficial choice for SEO professionals and website owners.
For anyone looking to improve their website’s performance in search engines, having the right tools is crucial. One such tool is Google Search Console, which provides website owners and SEO professionals with a detailed view of how their site interacts with Google Search.
With features that help you monitor search traffic, indexing status, and potential issues, it’s necessary for maintaining and optimizing a site’s SEO. Whether you’re managing a small blog or a large-scale business site, using this tool can help you rank higher in search engines.
What is Google Search Console?
Google provides a free tool, Google Search Console, to assist website owners and SEO specialists in monitoring and maintaining their site’s presence in Google Search results. It provides critical insights into how Google crawls and indexes a website, as well as detailed performance data such as search queries, click-through rates (CTR), and impressions.
The tool also highlights potential issues affecting a website’s search visibility, including indexing errors, mobile usability problems, and security concerns. With this tool, you can optimize your content, track site performance, and solve issues quickly to ensure your website ranks effectively in search results.
Most people tend to confuse Google Search Console with Google Analytics. To help you understand the difference, here’s a detailed comparison between both of them.
What is the difference between Search Console and Google Analytics?
Google Search Console and Google Analytics are both essential tools for understanding and improving a website’s performance, but they serve different purposes and offer distinct insights.
- Focus and purpose:
The Google Search Console (GSC) focuses on how Google views and interacts with your website. It provides data on search performance, indexing status, and technical issues that can affect a site’s ranking. However, Google Analytics (GA) primarily tracks and analyzes user behavior on your site, including traffic sources, user demographics, and interactions with your content.
- Data Type:
GSC gives you search-related data, like impressions, clicks, average position, and keyword performance, helping you understand how your site is performing in Google Search. However, GA offers in-depth insights into user activity, including pages visited, time spent on the site, conversion rates, and more.
What are the benefits of Google Search?
This tool offers several key benefits to website owners, helping them monitor and optimize their site’s presence on Google Search. Here are the top 6 main advantages:
- Improved Search Visibility: You can identify the keywords driving traffic to your site and the ranking of your pages by analyzing performance reports. This helps you optimize content for better search visibility.
- Indexing Monitoring: It offers comprehensive insights into the pages indexed by Google and identifies any problems. Preventing the proper indexing process. You can address indexing errors such as 404s, duplicate content, and crawl issues to guarantee your site’s complete indexation and visibility in search results.
- Technical SEO Insights: The tool helps identify technical issues such as mobile usability problems, slow page loading speeds, and security issues like malware or hacked content. This allows you to fix these problems before they impact user experience and rankings.
- Performance Tracking: You can track important metrics like impressions, clicks, CTR (click-through rate), and average position for specific keywords. This data helps in refining your SEO strategy to increase traffic and rankings.
- Sitemap Submission: Search Console enables the simple submission of XML sitemaps, helping Google crawl your site more efficiently. It also monitors and fixes sitemap issues.
- Rich Results Monitoring: If you are using structured data, such as schema markup, to improve your website’s search appearance, GSC offers valuable insights into the performance of your rich results, enabling you to optimize them for increased visibility.
Now that you have a clear understanding of Google Search Console’s functionality, it’s time to delve deeper into its features. Whether you’re a beginner and facing challenges, this guide will provide valuable insights to help you optimize your site’s performance and troubleshoot common issues. Let’s start with account creation.
Creating an Account
Setting up a Google Search Console account is simple and free, but it’s an essential step for monitoring your website’s performance in Google Search. To begin, follow these steps:
Sign in to Google Account: First, make sure to log into your Google account. If you don’t have one, you’ll need to create one.
Access Google Search Console: Visit the Google Search Console website and click on “Start Now” to begin the setup process.
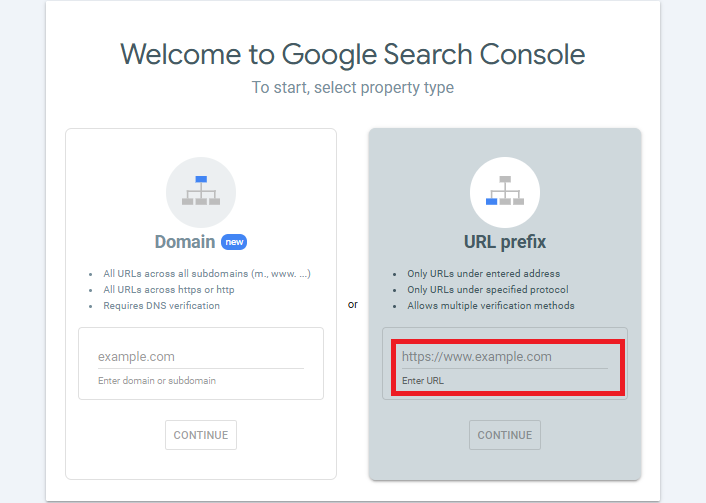
Add Your Website: Once logged in, click on “Add Property.” The system will prompt you to input the URL of your website. Google offers two types of property setups: Domain (which includes all subdomains and protocols) or URL prefix (for a specific version, such as www or non-www).
Verify Your Website: Verification is an important step to prove that you own the site. Google offers several verification methods, including uploading an HTML file to your website’s root directory, adding a DNS TXT record to your domain, or using Google Analytics or Google Tag Manager if they’re already set up on your site.
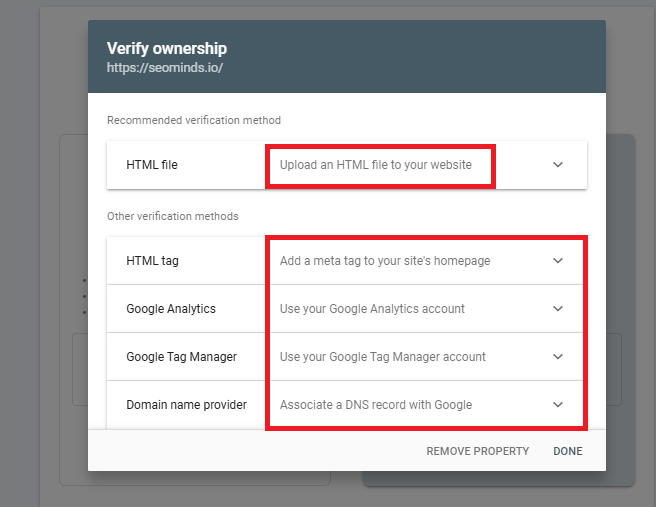
Submit for Review: After verification, Google will check the details and grant you access to your website’s data on Google Search Console.
If you find it challenging to add a property on Google Search Console, there’s an easier way: you can use the Google Site Kit plugin. This free WordPress plugin simplifies the setup by letting you connect your website to Google Search Console directly from your WordPress dashboard.
With just few clicks, Site Kit pulls in data from multiple Google tools, including Google Analytics and PageSpeed Insights, giving you insights on your site’s performance, search traffic, and speed without needing to leave WordPress. It’s an efficient, hassle-free solution to keep your website optimized and track key metrics effortlessly.
How to setup Google site Kit plugin?
Here are the steps to add the plugin to your website. First, log in to your WordPress website. Then, go to the “Plugins” section in the sidebar and click on “Add New.”
After selecting the Plugins button, a new page will appear with an option to add a new plugin in the top left corner. Simply click it.
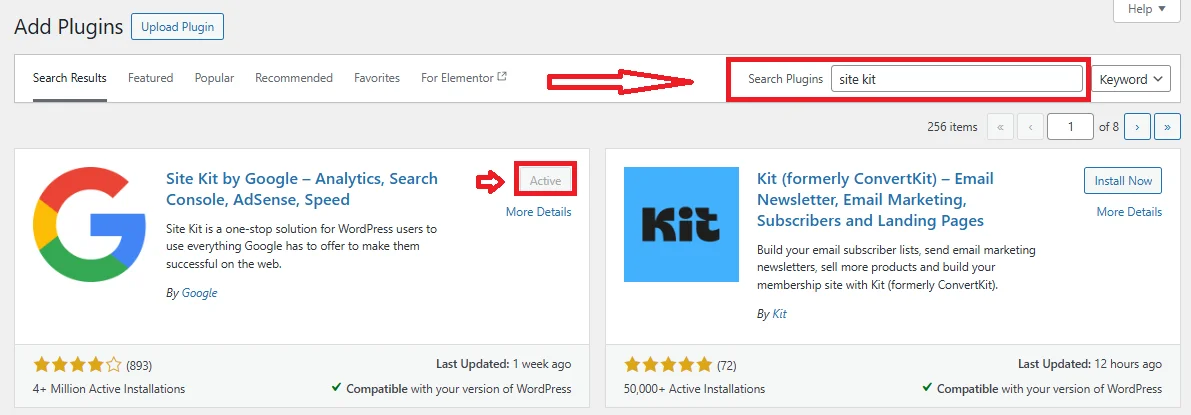
In the search bar, type “Google Site Kit” and, once it appears, click “Install Now.” After installation, click “Activate” to enable the plugin on your site.
Now that you have your account set up, you’re ready to start exploring its features and optimizing your website for better performance in Google Search.
Navigating the Dashboard
Once logged in, the dashboard serves as the central hub for all your website’s performance insights. Familiarizing yourself with the layout and available features is important for efficient navigation and analysis.
Key sections of the dashboard
The dashboard has multiple sections, each focused on a different area of performance or functionality:
- Performance: Here, you can monitor overall search traffic, assess keyword performance, and identify top-performing pages. This section is crucial for tracking the effectiveness of your SEO efforts over time.
- Index: This tab helps you understand how Google indexes your site’s pages. It displays the indexed pages and identifies potential problems that could hinder their visibility in search results.
- Experience: Google now emphasizes user experience, and this section provides insights into how well your site delivers on factors like mobile usability and Core Web Vitals.
- Enhancements: Here, you can view issues related to structured data, AMP, and mobile usability that affect search appearance.
Navigating the Dashboard
To maximize the benefits of GSC,
- Customize Reports: Use filtering options to target specific data, such as performance on mobile versus desktop or impressions from specific countries.
- Date Ranges: Adjust time ranges to track SEO trends over time or compare different time periods to gauge the impact of recent optimizations.
The user-friendly interface of GSC encourages you to explore the settings menu for options such as site verification, ownership management, and preference settings for specific notifications.
Deep Dive into Performance Reports
The Performance section provides critical insights into how your site is performing in Google Search, helping you analyze key metrics such as impressions, clicks, and CTR (click-through rate).
Metrics Explained: Impressions, Clicks, CTR, and Average Position
- Impressions: Google counts each time your website appears in its search results. Monitoring impressions can reveal the keywords that bring visibility to your site.
- Clicks: A click occurs when a user chooses your site from the search results. Tracking clicks helps you understand which queries are driving traffic.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): CTR is the percentage of impressions that result in clicks. A low CTR may indicate that your title tags and meta descriptions need improvement.
- Average Position: This metric represents your site’s ranking for a query, averaged across impressions. A lower average position means a higher ranking.
Search Queries and Keyword Analysis
GSC shows a list of search queries that drive traffic to your site. By examining these queries:
- Identify Target Keywords: Look for keywords that perform well and align them with content on your site.
- Optimize Low CTR Queries: If certain queries generate impressions but have low CTR, try optimizing meta descriptions or adding relevant content.
Device and Country Filters for Targeted Analysis
GSC lets you filter traffic by:
- Device: Break down traffic by device type to see if mobile or desktop users prefer certain pages.
- Country: This filter is useful for international SEO, as it shows how your content performs across regions.
Understanding Indexing and Coverage
Indexing is fundamental to SEO success, as it determines which pages Google includes in search results. The coverage report gives a detailed overview of indexing status.
How Google Indexes Your Site
When Google’s bots crawl your site, they decide which pages to include in its search index. Indexed pages are available in search results, while unindexed pages are not visible to users.
Reading the Coverage Report
The coverage report groups your pages into the following categories:
- Valid: Indexed and accessible in search results.
- Error: Pages that encountered problems during indexing (e.g., 404 errors).
- Excluded: Pages that are intentionally excluded, such as those with “noindex” tags.
Resolving Common Indexing Errors
Errors may include:
- Google cannot find broken links or deleted pages due to 404 errors. Use 301 redirects to address these issues.
- Server Errors (5xx): Temporary or recurring server problems. Check with your web host to resolve these issues.
Managing Crawl Budget
A “crawl budget” is the number of pages Google crawls during each visit to your site. Optimize crawl budget by:
- Removing Low-Value Pages: Eliminate duplicate or unnecessary pages to ensure Google focuses on valuable content.
- Ensuring Key Pages Are Accessible: Use internal links to guide crawlers toward high-priority pages.
Requesting URL Re-indexing
Use the URL Inspection Tool to submit URLs for re-indexing after making updates. This tool lets Google know to re-crawl these pages sooner than it would otherwise.
Submitting and Managing Sitemaps
A sitemap is a roadmap of your website that helps search engines find and index new content. Submitting a sitemap to GSC can improve crawl efficiency.
Why Sitemaps Matter for SEO
Sitemaps enhance your website’s crawlability, allowing Google to prioritize and find new or updated pages faster.
How to Submit Sitemaps in GSC
To submit a sitemap:
- Go to the Sitemaps section in GSC.
- Enter the URL of your XML sitemap.
- Click “Submit” to notify Google of the updated sitemap.
Monitoring Sitemap Status
Check the sitemap status regularly after submission to confirm the indexing of all important pages. Correct any errors, such as 404s, that could hinder the inclusion of specific pages in search results.
Best Practices for XML Sitemaps
- Avoid Duplicate Pages: Only include unique and valuable URLs.
- Organize Large Sites with Multiple Sitemaps: For large sites, create separate sitemaps for different sections.
The URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool is invaluable for checking the indexing status of individual pages and ensuring Google sees pages correctly.
How to Inspect URLs
This tool shows how Googlebot sees a specific page, allowing you to troubleshoot any issues that may affect indexing or ranking.
Submitting Pages for Re-Crawling
If you’ve updated a page, request re-crawling through the URL Inspection Tool to have changes reflected in search results more quickly.
Common Errors and Solutions
- Crawl Errors: Issues like blocked resources or incorrect redirects.
- Mobile Usability Errors: problems that prevent the page from being user-friendly on mobile devices.
Enhancements: Improving User Experience
Google emphasizes user experience (UX), and the Enhancements section provides insights into UX-related factors that impact SEO.
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals measure three aspects of user experience:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. Aim for an LCP below 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity. A good FID is below 100 ms.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. Keep CLS below 0.1 to prevent layout shifts.
Improving Mobile Usability
GSC identifies mobile usability issues such as:
- Small Text: Ensuring text size is legible on smaller screens.
- Interactive Elements Too Close: Buttons or links too close together, making it difficult for users to click accurately.
AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) Troubleshooting
If you use AMP, GSC identifies AMP-related errors that could affect your site’s mobile experience. Address any AMP issues to ensure optimal performance on mobile.
Structured Data Enhancements
Structured data helps your site appear as rich snippets. GSC highlights issues with your structured data, such as missing or invalid fields, allowing you to fix errors that impact search appearance.
Security and Manual Actions
GSC monitors security and manual action issues that can negatively impact your rankings.
Understanding Security Issues
Security issues, like malware or phishing, can harm your site’s rankings and deter visitors. Regularly check GSC for alerts about compromised content or security vulnerabilities.
What Are Manual Actions?
Google applies manual actions as penalties when a website violates its guidelines. They can lead to lower rankings or removal from search results.
Submitting a Reconsideration Request
Once you’ve resolved any issues that triggered a manual action, submit a reconsideration request to have the penalty lifted. GSC will notify you if the request is successful.
Link Reports: Building a Strong Link Profile
The Links report shows both external and internal links, giving you insight into your site’s link profile.
Analyzing Your Site’s Backlink Profile
External links, or backlinks, are a major factor in determining your site’s authority. The Links report shows which sites link to you and the anchor text they use.
Understanding Top Linking Sites
This section lists your top referring domains. High-quality sites linking to your pages indicate that your content is valuable and relevant.
Reviewing Internal Links
Internal links help Google understand the hierarchy of your content and how pages relate to each other. Ensuring you have a logical internal link structure is essential for SEO.
Enhancing Search Appearance with Structured Data
Structured data, or schema markup, provides extra context about your content, helping it appear in rich results.
Implementing and Testing Schema Markup
Use Google’s Rich Results Test to check if your schema markup is working. Implement common types like FAQ, Product, or How-To schema to enhance visibility.
Monitoring Structured Data Errors
GSC alerts you to errors in structured data, such as missing fields or unsupported values. Fix these to avoid missing out on rich results.
Now let’s talk about the Rapid URL Indexer:
What is Rapid URL Indexer?
Rapid URL Indexer (RUI) is a third-party tool designed to accelerate the indexing process of URLs by search engines like Google, Bing, and others. It provides a faster alternative to Google Search Console by using advanced techniques such as proxy networks, backlink generation, and social media signals. While Google Search Console remains essential for managing a website’s presence and monitoring performance, RUI focuses solely on getting URLs indexed quickly and efficiently.
Key Features of Rapid URL Indexer:
- Fast URL Indexing:
RUI automates the submission of URLs and speeds up the crawling process by search engines. It mimics natural search engine behavior, ensuring faster indexing of new or updated content. - Bulk URL Submission:
One of RUI’s standout features is its ability to handle bulk submissions, allowing users to submit hundreds or thousands of URLs at once. This saves significant time compared to manual submissions via Google Search Console. - Advanced Techniques:
RUI uses proxies, IP rotation, and automated backlink generation to signal search engines to crawl and index your URLs faster. Social media signals are also utilized to increase content visibility and improve indexing rates. - User-Friendly Interface:
Unlike Google Search Console, which requires some technical knowledge, RUI is designed to be beginner-friendly. Its simple interface enables quick submissions and tracking without deep technical expertise. - Multi-Search Engine Support:
While Google Search Console focuses only on Google, RUI supports multiple search engines, including Bing, Yahoo, and DuckDuckGo, helping improve overall search visibility.
Benefits of Rapid URL Indexer:
- Faster Indexing: Speeds up the process, with some URLs indexed within hours or even minutes.
- Efficient for Large Websites: Ideal for websites with high volumes of content, allowing bulk URL submissions.
- Boosts Crawl Frequency: Generates backlinks and signals search engines to crawl pages more often.
- Easy to Use: Designed for SEO professionals and beginners alike, with minimal setup.
- Cost-Effective: While it’s a paid tool, the speed and efficiency it offers make it a valuable addition for large-scale SEO campaigns.
How Does Rapid URL Indexer Work?
RUI replicates the crawling behavior of search engines to expedite the indexing process. It uses proxies and IP rotation to simulate real user interactions, avoiding detection as spam. Backlinks are generated, and URLs are promoted on social platforms to enhance visibility and encourage faster indexing.